Although lives have been saved due to the discovery of endotoxin removal methods including solvent extraction and affinity adsorption, they have limitations in treatment capacity, efficiency or costs. Endotoxin contaminations still result in a large number of deaths in global every year. This necessitated a mechanistic breakthrough for endotoxin removal or inactivation. Herein, we engineered a dephosphorylation reaction on endotoxins by a synthetic nano-catalyst (CeO2) to attenuate the toxicity. CeO2 prepared in phosphate-free hydrothermal reaction selectively and efficiently catalyzed the breaking of P-O bonds in endotoxins. Catalytic depletion of phosphates from endotoxins attenuated their binding with Toll-like receptors, NF-κB activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine release. Airborne LPS was, for the first time, inactivated (98%) by this facile dephosphorylation reaction. A CeO2 integrating column displayed a 16-fold higher treatment capacity than commercial resins to aqueous endotoxins (water and protein solution). Overall, our findings offer a different mechanistic insight for removal of endotoxins.
This work has been pulished in Nano Today with the title of "Engineering catalytic dephosphorylation reaction for endotoxin inactivation".(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1748013222000834.)
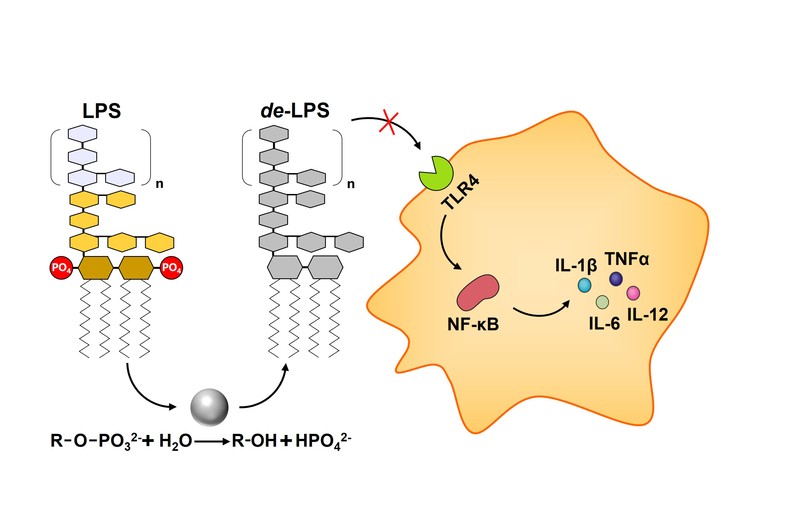
CeO2 NPs catalytically inactivated endotoxins with decreased immunotoxicity